Steam engines rely on external heat sources to generate power, using large boilers and bulky designs, while internal combustion engines burn fuel inside cylinders, making them more compact and efficient. The shift from steam to internal combustion ushered in faster, portable transportation and industry advancement, but both face environmental concerns due to fossil fuel use. Exploring these differences reveals how ongoing innovations aim to create cleaner, more sustainable engine technologies—stay tuned to uncover how this progression shapes the future.
Key Takeaways
- Steam engines rely on external heat to generate steam, while internal combustion engines burn fuel directly inside cylinders for power.
- Internal combustion engines are more compact, efficient, and suitable for modern transportation compared to bulky steam engines.
- Steam engines face sustainability challenges due to fossil fuel dependence, whereas internal combustion engines contribute significantly to pollution.
- Transitioning from steam to internal combustion engines marked a move toward portability, efficiency, and large-scale industrial use.
- Both technologies are advancing toward sustainability, with electric motors emerging as a future alternative to traditional engines.
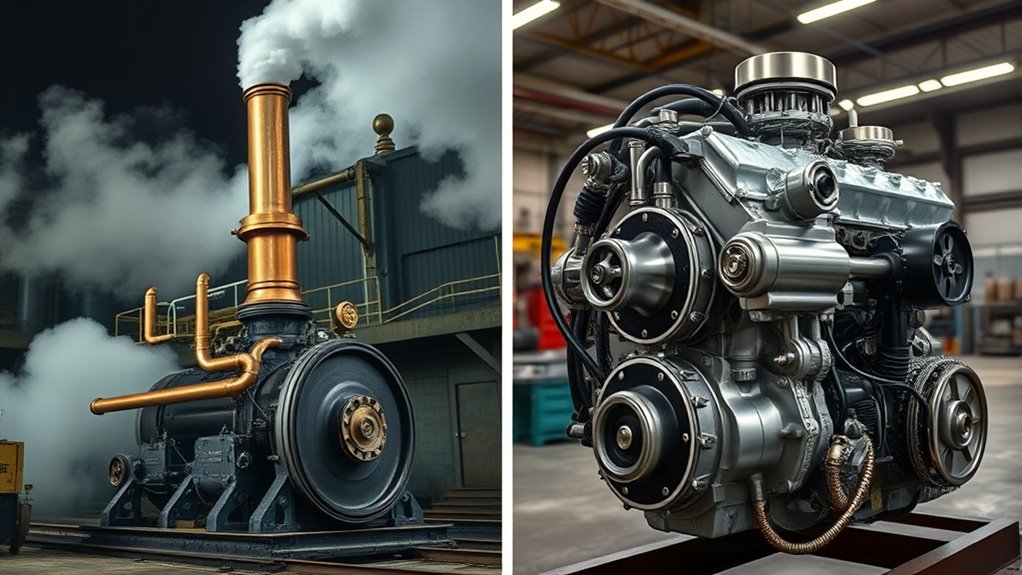
When comparing steam engines and internal combustion engines, understanding how each technology operates and their respective advantages is vital. Steam engines rely on boiling water to create steam, which then pushes pistons or turbines to generate power. Internal combustion engines, on the other hand, burn fuel directly inside cylinders, causing controlled explosions that drive pistons. This fundamental difference influences not only their design and efficiency but also their environmental impact and infrastructure needs.
Steam engines were the pioneers of industrial power, but they face significant sustainability challenges today. They typically burn coal, wood, or other fossil fuels, which produce high levels of greenhouse gases and pollutants. Their reliance on large-scale boilers and extensive piping infrastructure also demands significant infrastructural investments. These engines require a steady supply of water and fuel, and their heavy, bulky design makes them less adaptable to modern transportation needs. As a result, steam engines are largely phased out in favor of more efficient, cleaner options.
Steam engines face sustainability challenges due to fossil fuel reliance and infrastructure demands.
Internal combustion engines have dominated transportation for over a century, largely because of their higher efficiency and smaller size. They are more suitable for vehicles, ships, and small-scale power generation because they can produce a lot of power with less fuel and in a compact form. However, they are not without their own sustainability challenges. Internal combustion engines burn fossil fuels, releasing carbon dioxide and other pollutants into the atmosphere. Despite advancements like electric starters and fuel injection, their dependence on oil remains a major environmental concern. Furthermore, the infrastructural demands for fueling and maintenance are significant, requiring extensive networks of gas stations and repair facilities.
The shift from steam to internal combustion engines marked a movement toward more practical, portable, and efficient power sources. Internal combustion engines revolutionized transportation and industry by reducing the size and complexity of machinery, enabling mass production and mobility. However, as awareness around sustainability grows, both technologies face scrutiny. Steam engines, with their cleaner potential if powered by renewable sources, highlight the importance of developing sustainable energy solutions. Meanwhile, internal combustion engines are increasingly being replaced or supplemented by electric motors, which promise to address their environmental impact while relying on existing electrical infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Maintenance Costs Compare Between Steam and Internal Combustion Engines?
You’ll find that maintenance routines for steam engines tend to be more complex and frequent, leading to higher cost implications. Steam engines require regular inspections, boiler upkeep, and component replacements, which can add up quickly. In contrast, internal combustion engines generally have simpler maintenance routines, with fewer parts needing regular attention, resulting in lower ongoing costs. Overall, steam engines typically incur higher maintenance costs due to their more intricate and demanding upkeep.
What Are the Environmental Impacts of Each Engine Type?
Imagine your engine as a champion of pollution, either belching smoke like a dragon or quietly sneaking out emissions. Steam engines, fueled by coal, release hefty greenhouse gases, while internal combustion engines emit carbon dioxide and other pollutants. Though stricter emission regulations push for greener solutions, both harm the environment. Renewable alternatives like electric engines promise a cleaner future, making your current engine’s impact look like a bad joke.
Which Engine Type Offers Better Fuel Efficiency?
You’ll find that internal combustion engines generally offer better fuel efficiency based on efficiency metrics and fuel consumption. They convert more of the fuel’s energy into useful work, making them more effective for everyday use. Steam engines tend to have higher fuel consumption and lower efficiency due to energy losses. Hence, if you’re aiming for improved fuel efficiency, internal combustion engines are the better choice, especially with modern advancements.
How Do Startup Times Differ Between Steam and Internal Combustion Engines?
You’ll notice steam engines have longer startup times due to boiler warm-up and ignition delay, which can be inconvenient if you need quick readiness. Internal combustion engines start faster because they don’t require extensive warm-up; their ignition delay is minimal. While steam engines take more time to reach prime operation, many appreciate their smooth power delivery once running. For rapid starts, internal combustion engines generally outperform steam.
What Are the Safety Concerns Associated With Steam Versus Internal Combustion Engines?
You should be aware that steam engines carry safety risks like boiler explosions, which can be catastrophic if not properly maintained. They also produce toxic emissions, such as smoke and steam pollutants, which pose health hazards. Internal combustion engines, on the other hand, have concerns like fuel leaks and exhaust gases that can be harmful. Ensuring proper safety measures helps minimize these risks for both types of engines.
Conclusion
Ultimately, choosing between steam and internal combustion engines is like picking between a reliable old friend and an exciting new adventure. Steam engines, with their historical charm, remind us of innovation’s roots, while internal combustion engines offer speed and efficiency for today’s needs. As technology advances, you’ll find that each has its place, but the future likely belongs to cleaner, more sustainable solutions. Embrace the shift, knowing that progress is as constant as the steam rising from a kettle.








